acetabular labral tear special tests|acetabular labral calcification radiology : specialty store This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability .
WEBNo hay opciones para ver El fin del amor gratis online actualmente en México. Puedes seleccionar "Gratis" y pulsar la campana para recibir una notificación cuando show esté disponible para ver sin coste en servicios de streaming y TV. Si está interesado en ver otras películas y series gratuitas online hoy mismo, puede:
{plog:ftitle_list}
webFicou na dúvida e não sabe se uma bet é confiável ou não? Dê uma olhada no rodapé do seu site. Todas as casas de apostas devem mostrar para os jogadores que possuem uma licença de jogo.
A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally .
There are a number of clinical tests and subjective pieces of information that clinicians may associate with labral pathology of the hip. Fortunately Burgress and crew . The hip labrum (also known as the acetabular labrum) is a ring of tough fibrocartilage that covers the rim of the acetabulum. It serves as a gasket between the acetabulum and head of the femur, creating a vacuum seal and .Introduction. Acetabular labrum tears (labral tears) can cause pain, stiffness, and other disabling symptoms of the hip joint. The pain can occur if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. Active . Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They .
This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability .Arthroscopy remains the reference standard for diagnosing acetabular labral tears allowing for dynamic examination and assessing the extent of the tear [50, 52]. However, it is more . Impingement tests and MRA have high sensitivity and accuracy in clinical diagnosis of labral tears. Arthroscopic debridement, repair and osteoplasty for labral tears .
right superior acetabular labral tear
Fortunately, treatments are available for hip labral tears, including nonsurgical and surgical options. . The hip labrum (also known as the acetabular labrum) is a ring of tough fibrocartilage that covers the rim of the acetabulum. . These .management of acetabular labral tears is lacking [4, 10, 11]. With the advent of new arthroscopic techniques, focus on treatment of acetabular labral tears has most commonly featured arthroscopic labral repair or debridement [3, 4]. Despite the growing body of evidence for surgical treat-ment, there is still an incomplete understanding as to opti- Labral tears may cause a popping, catching, or clicking sound associated with activities such as dance, gymnastics, hockey, basketball, and soccer. 2, 5, 9 Physical examination for labral tears .Impingement Test. As part of the physical examination, your doctor will likely conduct the impingement test. For this test, your doctor will bring your knee up toward your chest and then rotate it inward toward your opposite shoulder. If this re-creates your hip pain, the test result is positive for impingement.
A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.
Hip labral tears are a sports-related injury that affects athletes who participate in high-impact sports, but they can affect anyone. . If the labral tear diagnosis is still unclear after these tests, your doctor may recommend an ultrasound-guided injection with a painkiller. If it relieves pain, then it is likely that the cause is a labral . The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip joint by increasing the articular surface of the joint and the depth of the acetabulum and creating a suction-seal effect on the femoral head [1,2,3,4].While acetabular labral tears are prevalent in both symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals, the prevelence is slightly higher in symptomatic individuals (62% .acetabular impingement, labral tears, and gluteus medius tendon tears typically have good surgical outcomes, advanced imaging and/or early referral may improve patient outcomes. (Am Fam Physician .Acetabular labrum tears (ALT) are present in 22–55% of individuals with hip or groin pain. Tears can occur as a result of trauma or degeneration and are markedly associated with femoral acetabular morphological variations. An ALT can lead to biomechanical deficiencies and a loss of stability to the coxafemoral joint due to the labrum serving as a stabilising structure of this joint. .
Hip Labral Tear Tests. Specific clinical tests are used to check for labral tears and understand the potential location of the tear (tears in front vs tears at the back). Three common hip labral tear tests performed in a clinic or doctor’s office include: Hip labral tear test 1: Twist test 1 O’Connor FG, Wilder RP, Nirschl R, eds. Running . Labral tears in the hip are now becoming widely recognised as a source of anterior hip/groin pain and intra-articular pathology. The prevalence of acetabular labral tears in some populations presenting with hip or groin pain has been reported to be between 22% and 55% (Narvani et al., 2003; McCarthy et al., 2001). A hip (acetabular) labral tear is damage to cartilage and tissue in the hip socket. The labrum is a band of tough cartilage and connective tissue that lines the rim of the hip socket, or acetabulum.
Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, . Biceps tendinopathy or Superior labral tears Speed's Test; References [edit | edit source] ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Magee, D. Shoulder. Chapter 5 In: Orthopedic Physical Assessment. Elsevier, 2014View our orthopaedic doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating shoulder labral tears. Types of Labral Tears of the Shoulder. There are several areas around the glenoid where a shoulder labral tear can occur: Bankart tear: A Bankart tear or lesion occurs at the front/lower part of the glenoid. Posterior labrum tear: This tear occurs at . All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular labral tears 7 was developed earlier than the FADER and FABER tests. Although a positive McCarthy test is not very common in labral lesions, it has a high specificity.
This statement summarises and appraises the evidence on diagnostic tests and clinical information, and non-operative treatment of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) syndrome and labral injuries. We included studies based . A hip labral tear usually occurs when the labrum is worn down and injured due to repetitive motion. Learn about common causes, diagnosis and treatment. . Also known as the acetabular labrum, this should not be confused with the labrum of the shoulder, which is a similar structure called the glenoid labrum.Acetabular labral tears are a common cause of hip pain. 1–3 In athletes, hip injuries represent 3.1% to 8.4% of sports injuries in recent reports. 4,5 The prevalence of labral tears in patients with hip complaints has been reported from 22% to 55%. 6,7 The understanding of labral tears has greatly evolved in the past few years, and there now is better understanding of labral .
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B. Acetabular labral tears represent the most common cause for mechanical hip symptoms – in a recent study, they were found to be the cause of groin pain in more than 20% of athletes presenting with groin pain. Acetabular Labral Tear Classification. Labral tears can be classified according to location, etiology, and type: Location:England’s Ruben Loftus-Cheek holds his hip, 2017 Mechanical disruption of the hip joint is often related to an acetabular labral tear (ALT) and can be associated with intraarticular snapping hip syndrome in up to 80% of cases (1). Labral tears affecting the hip joint are prevalent in 22-55% of patients with hip or groin pain and evidence suggests that an untreated ALT may predispose .
patients with a labral tear. 5. The anterior-superior region of the joint is the most common location for a labral tear, 33. the patient symptoms of which are provoked by combined hip internal rotation, ad-duction, and flexion. 28. Labral chondral lesions may also re-sult from atraumatic hip instability, with or without mechanical impingement.
It should be noted that the starting and ending positions for posterior labral tears are the same positions as the labral anterior and posterior impingement tests, so an individual with femoral acetabular impingement will test positive on this test as well. Note: this test should only be performed be properly trained health care practitioners.The population with a combination of cam and pincer often suffer from a slipped capital femoral epiphysis called the S C F E. They show varying degrees of hip impingement. An estimated 85% of patients with FAI have this type of mixed morphology, although Raveendran et al. found only 2% of subjects in their prospective longitudinal cohort study had mixed morphology (albeit in a . Interpretation The impingement test is helpful in identifying acetabular labral tears. If this test is negative and if a labral tear is still suspected, ultrasound can reliably diagnose most tears of the acetabular labrum. MR arthrography is indicated in cases where ultrasound is negative, but the patient suffers continued, specific symptoms.Acetabular labrum tears (ALT) are present in 22-55% of individuals with hip or groin pain. . Examination of acetabular labral tear: a continued diagnostic challenge Br J Sports Med. 2014 Feb;48(4) :311-9 . clinical examination and special test findings that are unique to the condition. Imaging methods such as MRI, CT and ultrasonography .
Magnetic resonance arthrography is the diagnostic test of choice for labral tears. . Della Rocca GJ, Prather H, et al. Clinical presentation of patients with tears of the acetabular labrum.
labral tear mri images
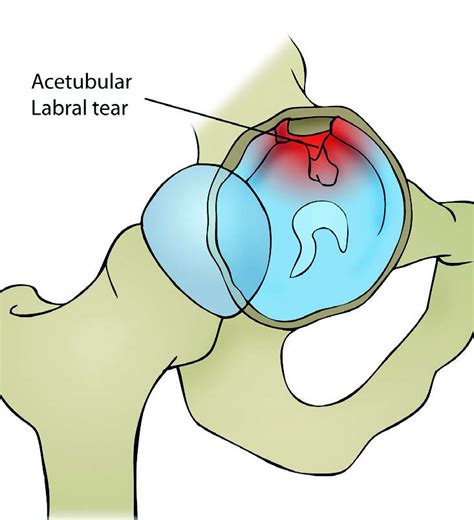
grades of hip labral tears
video of rear impact with gerry can test
Jogadores mais valiosos Campeonato Brasileiro Série A - Po.
acetabular labral tear special tests|acetabular labral calcification radiology